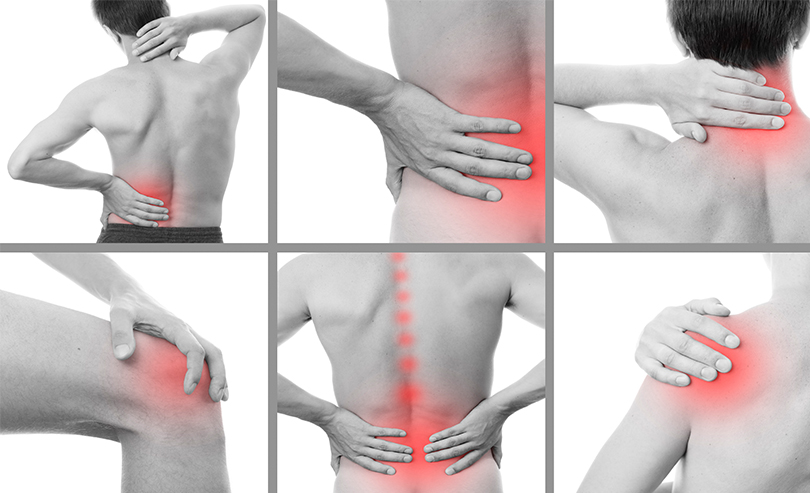
Arthritis in the Back
Arthritis itself is a degenerative disease that can affect an individual’s joints. The cartilage that normally cushions the tops of the bones has been worn down. This means that the bones and nerves are no longer protected from the general impact or grind placed on them through movement.
Over time, these impacts can cause pain and swelling around the joints. However, arthritis in the back can cause pain with every movement, because the back is linked to so much of what we do every day.
Arthritis in the Back Symptoms
When arthritis targets the joints in your neck and back, the pain can often be directly associated with the immediate joints. Pain or stiffness when moving felt along the back is common in individuals that are experiencing arthritis. However, individuals may have differing levels of symptoms depending on arthritis’ progression.
Although pain and stiffness can be localized, people may also have symptoms that manifest elsewhere in the body. Many people experience numbness or tingling in their arms and legs.
This occurs when arthritis interferes with the nerves or even the spinal cord itself. The effects to the extremities can also lead to a decrease in motor function or strength as people try to move less to avoid the unpleasant sensations.
The pain and numbness can often be reduced or alleviated when the individual lies down. This reduces the pressure on the joints allowing for some temporary relief.
Many people also experience symptoms outside of actual physical pain or discomfort. People may begin to withdraw from social settings or be unable to participate in daily activities. The reduction in their abilities can also lead to depression, general unhappiness, or a decrease in job performance.
Causes of Arthritis in the Back
Several known factors can contribute to being at a higher risk of developing arthritis in the back. For individuals that are in their youth, arthritis is typically caused by a genetic defect or an injury that affect the bodies’ ability to cushion the vertebrae in the spinal column.
Arthritis can also be associated with aging as a natural process. When individuals are under 45 years old, men are more likely to experience arthritis. When people are older than 45, the distribution switches to women.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic, progressive and delibating type of arthritis that affects the spine. Read on to learn more about it here.
In addition to aging, other factors may affect your risk of developing arthritis. Excess weight plays a role due to the increased pressured that is constantly placed on the joints.
Additionally, people that play sports or have careers that involve repetitive motions are at an increased risk for developing arthritis. As people repeat the same movements, the cartilage responsible for bracing impacts is gradually worn down.
Treatment for Arthritis in the Back
Fortunately, there are several different treatment options available if you or a loved one has been diagnosed with arthritis in the back. The goal of back-related arthritis treatment is generally to reduce the amount of pain that you experience due to your arthritis and be able to have a healthy lifestyle.
Some things that you may explore in your treatment options are:
- Managing weight – Simply reducing your weight reduces the workload that your joints must perform.
- Get on an Exercise Regimen – While you will want to avoid activities that place undue stress on your joints, you have several different options of activities that will help to strengthen your body without compromising your joints. Exercise is further broken down into specific targets. There are also plenty of exercises for arthritis you can find online too.
- Strengthening Exercises – These exercises try to make the specific muscles that aid your arthritic joints stronger. The muscles may then be able to compensate for the reduction in cartilage support.
- Aerobic Exercises – These workouts are designed to make your heart and circulatory system perform better.
- Range of Motion Exercises – As people experience arthritis, they often attempt to reduce movements that make them uncomfortable. Reducing our movement ends up making us even stiffer. These exercises are aimed at getting you to be able to maintain or increase your ability to move your body and joints.
Specific exercises that may be a part of your regimen include swimming, bicycling, lifting weights, or using resistance bands. If you are properly guided, these workouts can be low impact for your back joints.
In addition to diet and exercise, there are several other options that you can discuss with your doctor. To effectively manage pain, discomfort, and numbness, your doctor may prescribe you medications aimed at pain management or swelling reduction. These medications include over the counter options and some prescription options. Prescription medications could be painkillers, mild narcotic medications, or steroidal injections around the spinal column.
Finally, many people also find back-related arthritis pain relief through massage, acupuncture or using hot and cold compresses. If you have been diagnosed with arthritis in your back, it may be worthwhile to explore options and find what works best for you.
Overview
If you or somebody you know has been experiencing pain in their back, it’s a good idea to get it checked by a medical professional. Discuss your concerns with your healthcare professional and be open to their suggestions for improving your lifestyle.
When treatment options are started earlier, there is a broader range of available options and a better chance of slowing the progression of arthritis.